24 - 內置模塊
📄目錄
24 - 內置模塊📄目錄1 os模塊1.1 os.name 返回操作系統類型1.2 os.getenv 環境變量名稱1.3 os.path.split() 把目錄名和文件名分離1.3.1 os.path.dirname()1.3.2 os.path.basename()1.4 os.path.exists() 判斷路徑(文件/目錄)是否存在1.5 os.path.isfile() 判斷是否存在文件1.6 os.path.isdir() 判斷目錄是否存在1.7 os.path.abspath() 獲取當前路徑下的絕對路徑1.8 os.path.isabs() 判斷是否絕對路徑2 sys模塊2.1 sys.getdefaultencoding() 獲取系統默認編碼格式2.2 sys.path 獲取環境變量的路徑,跟解釋器相關2.3 sys.platform 獲取操作系統平台2.4 sys.version 獲取python解釋器的版本信息3 time模塊3.1 time.sleep() 延時操作,以秒為單位3.2 time.time() 獲取到當前的時間戳3.3 time.localtime() 將一個時間戳轉換為當前時區的struct_time3.4 time.asctime() 獲取系統當前時間3.5 time.ctime() 獲取系統當前時間/把時間戳轉換成固定的字符串表達式3.6 time.strftime(格式化字符串, struct_time) 將struct_time轉換為時間字符串3.7 time.strptime(時間字符串,格式化字符串) 將時間字符串轉換成struct_time4 logging模塊4.1 logging中的等級/級別排序4.2 logging.basicConfig() 配置root_logger的參數4.2.1 filename 指定日誌文件的文件名4.2.2 filemode 文件的打開方式4.2.3 level 指定日誌顯示級別,默認是警告信息warning4.2.4 format 指定日誌信息的輸出格式5 random:隨機模塊5.1 random.random() 產生大於0且小於1之間的小數5.2 random.uniform() 產生指定範圍的隨機小數5.3 random.randint() 產生指定範圍內的隨機整數(含首尾)5.4 random.randrange(start, stop, [step])導航連結:
1 os模塊
💡 作用:用於和操作系統進行交互
通用操作:
獲取平台信息
對目錄的操作
判斷操作
導入os模塊
xxxxxxxxxximport os1.1 os.name 返回操作系統類型
功能:指示正在使用的工作平台(返回操作系統類型)

xxxxxxxxxxprint(os.name) # 對於Windows,返回nt;對於Linux,返回posix輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxposix1.2 os.getenv 環境變量名稱
功能:讀取環境變量

xxxxxxxxxxprint(os.getenv("PATH")) # 在Linux/Mac,要大寫PATH,Windows上可以小寫1.3 os.path.split() 把目錄名和文件名分離
功能:把目錄名和文件名分離,以元組的形式接收,第一個元素是目錄路徑,第二個元素是文件名

xxxxxxxxxxa = os.path.split(r"/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice/py53.py")print(type(a), a)輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx<class 'tuple'> ('/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice', 'py53.py')1.3.1 os.path.dirname()
功能:顯示split分割的第一個元素,即目錄

xxxxxxxxxxprint(os.path.dirname(r"/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice/py53.py"))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice1.3.2 os.path.basename()
功能:顯示split分割的第二個元素,即文件名

xxxxxxxxxxprint(os.path.basename(r"/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice/py53.py"))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxpy53.py⚠️ 如果路徑以/結尾,那麼返回空值;如果以\結尾,則報錯。
1.4 os.path.exists() 判斷路徑(文件/目錄)是否存在
存在:返回True
不存在:返回False

xxxxxxxxxxprint(os.path.exists(r"/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice"))print(os.path.exists(r"/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice/py53.py"))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxTrueTrue1.5 os.path.isfile() 判斷是否存在文件
❗ 找目錄會返回False,而且只能使用絕對路徑

xxxxxxxxxxprint(os.path.isfile(r"/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice/py53.py"))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxTrue1.6 os.path.isdir() 判斷目錄是否存在
❗ 找文件會返回False,而且只能使用絕對路徑

xxxxxxxxxxprint(os.path.isdir(r"/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice"))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxTrue1.7 os.path.abspath() 獲取當前路徑下的絕對路徑

xxxxxxxxxxa = os.path.abspath("py54.py")print(a)print(os.path.isabs(a))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice/py54.pyTrue1.8 os.path.isabs() 判斷是否絕對路徑
已在1.7展示
2 sys模塊
💡 作用:負責程序跟python解釋器的交互
導入sys模塊
xxxxxxxxxximport sys2.1 sys.getdefaultencoding() 獲取系統默認編碼格式

xxxxxxxxxxprint(sys.getdefaultencoding())輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxutf-82.2 sys.path 獲取環境變量的路徑,跟解釋器相關

xxxxxxxxxxprint(sys.path) # 以列表形式返回輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx['/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice', '/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice', '/Applications/PyCharm.app/Contents/plugins/python-ce/helpers/pycharm_display', '/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11/lib/python311.zip', '/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11/lib/python3.11', '/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11/lib/python3.11/lib-dynload', '/Users/Myname/Documents/Coding/PyCharm/PyPractice/.venv/lib/python3.11/site-packages', '/Applications/PyCharm.app/Contents/plugins/python-ce/helpers/pycharm_matplotlib_backend', '/Applications/PyCharm.app/Contents/plugins/python-ce/helpers/pycharm_plotly_backend']第一項為當前所在的工作目錄
可以用以下形式獲取特定資訊,如:print(sys.path[0])
2.3 sys.platform 獲取操作系統平台

xxxxxxxxxxprint(sys.platform)輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxdarwin2.4 sys.version 獲取python解釋器的版本信息

xxxxxxxxxxprint(sys.version)輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx3.11.9 (v3.11.9:de54cf5be3, Apr 2 2024, 07:12:50) [Clang 13.0.0 (clang-1300.0.29.30)]3 time模塊
👉🏻 時間顯示格式的調用或轉換方式
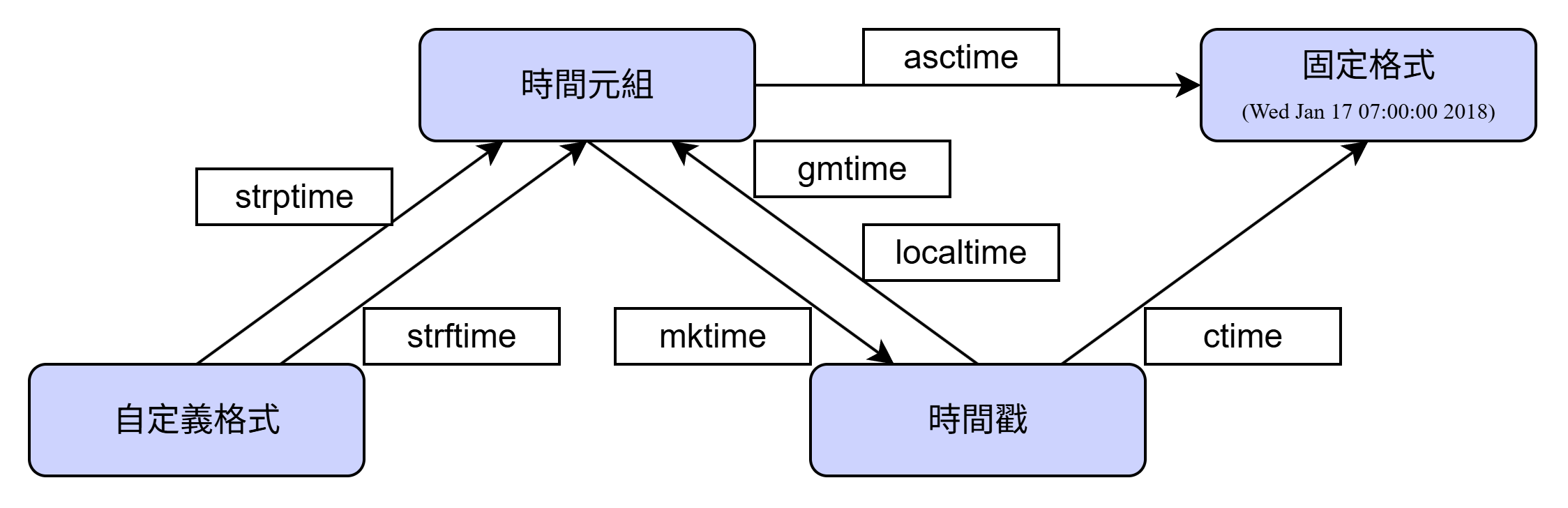
導入time模塊
xxxxxxxxxximport time💡 三種時間表示:
時間戳(timestamp)
格式化的時間字符串(format time)
時間元組(struct_time)
3.1 time.sleep() 延時操作,以秒為單位

xxxxxxxxxxprint(12)time.sleep(1)print(123) # 兩次輸出之間停留一秒輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx121233.2 time.time() 獲取到當前的時間戳
💡 以秒計算,從1970年1月1日 00:00:00開始計算

xxxxxxxxxxprint(time.time(), type(time.time()))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx1754922368.013939 <class 'float'>3.3 time.localtime() 將一個時間戳轉換為當前時區的struct_time

xxxxxxxxxxprint(time.localtime())t = time.localtime()print(t[0], t.tm_hour, t.tm_min, t.tm_sec)輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxtime.struct_time(tm_year=2025, tm_mon=8, tm_mday=11, tm_hour=22, tm_min=30, tm_sec=29, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=223, tm_isdst=0)2025 22 30 29tm_wday:一周中的第幾天(周一為0)tm_yday:一年中的第幾天tm_isdst:夏令時
3.4 time.asctime() 獲取系統當前時間

xxxxxxxxxxprint(time.asctime(), time.asctime(time.localtime()), sep="\n") # 可以將時間元組轉換為固定的字符串表達式輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxMon Aug 11 22:32:05 2025Mon Aug 11 22:32:05 20253.5 time.ctime() 獲取系統當前時間/把時間戳轉換成固定的字符串表達式

xxxxxxxxxxprint(time.ctime())t = time.time()print(t)print(time.ctime(t))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxMon Aug 11 22:36:35 20251754922995.6886249Mon Aug 11 22:36:35 20253.6 time.strftime(格式化字符串, struct_time) 將struct_time轉換為時間字符串
| 格式符號 | 含義 |
|---|---|
| %a | 星期簡寫(Mon,Sun) |
| %A | 星期全稱(Monday,Sunday) |
| %b | 月份簡寫(Jun,Aug) |
| %B | 月份全稱(June,August) |
| %c | 日期時間的字符串表示 |
| %d | 一個月的第幾天(0-31) |
| %H | 時,24小時制 |
| %I | 時,12小時制 |
| %j | 一年中的第幾天(001-366) |
| %m | 月份(01-12) |
| %M | 分鐘(00-59) |
| %p | 本地am或者pm的相應符 |
| %S | 秒(00-59) |
| %U | 一年中的星期數(00-53);第一個星期天之前為第0周 |
| %w | 一周中的第幾天(0-6,0為星期天) |
| %W | 與%U相同,但以星期一為周首 |
| %x | 本地相應日期字符串(DD/MM/YY) |
| %X | 本地相應日期字符串(HH:MM:SS) |
| %y | 去掉前兩位的年份(00-99) |
| %Y | 完整年份(XXXX) |
| %z | 與UTC時間的間隔(如果是本地時間,返回空字符) |
| %Z | 時區名(如果是本地時間,返回空字符) |
| %% | %字符 |

xxxxxxxxxxprint(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()))t = time.strftime("%c", time.localtime())print(t)輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx2025-08-11 23:05:15Mon Aug 11 23:05:15 20253.7 time.strptime(時間字符串,格式化字符串) 將時間字符串轉換成struct_time

xxxxxxxxxxt = time.strptime("1970-01-01", "%Y-%m-%d")print(t, type(t))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxtime.struct_time(tm_year=1970, tm_mon=1, tm_mday=1, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=3, tm_yday=1, tm_isdst=-1) <class 'time.struct_time'>4 logging模塊
導入logging模塊
xxxxxxxxxximport logging💡 作用:用於記錄日誌信息
💡 日誌的作用:
程序調試
了解軟件程序運行情況是否正常
軟件程序運行故障分析與問題定位
4.1 logging中的等級/級別排序
| Level | vaule | describe |
|---|---|---|
| NOTEST | 0 | 不設定級別,按照父logger的級別顯示日誌。如果是root logger,那麼就會顯示所有的日誌 |
| DEBUG | 10 | 程序的詳細調試信息,調試代碼會用到 |
| INFO | 20 | 普通信息,確定程序是否按照正常的運行 |
| WARNING | 30 | 程序發出警告,表示發生意想不到的事情或者指示接下來可能會出現一些問題,但是還能正常運行 |
| ERROR | 40 | 程序發生錯誤,某些功能無法運行 |
| CRITICAL(FATAL) | 50 | 程序出現致命錯誤,無法運行 |
💡 CRITICAL(FATAL) > ERROR > WARNING > INFO > DEBUG > NOTEST

xxxxxxxxxxlogging.debug("debug message")logging.info("info message")logging.warning("warning message")logging.error("error message")logging.critical("critical message")輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxxWARNING:root:warning messageERROR:root:error messageCRITICAL:root:critical message❗ logging默認的level就是warning,logging只會顯示級別大於等於warning的日誌信息
4.2 logging.basicConfig() 配置root_logger的參數
4.2.1 filename 指定日誌文件的文件名
所有會顯示的日誌都會存在到這個文件中去

xxxxxxxxxxlogging.basicConfig(filename = "log.log") # 在當前目錄下生成log.log文件,並寫入日誌信息logging.debug("debug")logging.info("info")logging.warning("warning")logging.error("error")logging.critical("critical")輸出結果(在log.log文件中):
xxxxxxxxxxWARNING:root:warningERROR:root:errorCRITICAL:root:critical4.2.2 filemode 文件的打開方式
默認是a(追加模式)
w:只寫模式(原本有就覆蓋)

xxxxxxxxxxlogging.basicConfig(filename = "log.log", filemode= "a")4.2.3 level 指定日誌顯示級別,默認是警告信息warning

xxxxxxxxxxlogging.basicConfig(filename = "log.log", filemode="w", level = logging.NOTSET)logging.debug("debug")logging.info("info")logging.warning("warning")logging.error("error")logging.critical("critical")輸出結果(在log.log文件中):
xxxxxxxxxxDEBUG:root:debugINFO:root:infoWARNING:root:warningERROR:root:errorCRITICAL:root:critical4.2.4 format 指定日誌信息的輸出格式
| 格式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| %(levelno)s | 打印日誌級別的數值 |
| %(levelname)s | 打印日誌級別名稱 |
| %(pathname)s | 打印當前執行程序的路徑 |
| %(filename)s | 打印當前執行程序名稱 |
| %(funcName)s | 打印日誌的當前函數 |
| %(lineno)d | 打印日誌的當前行號 |
| %(asctime)s | 打印日誌的時間 |
| %(thread)d | 打印線程ID |
| %(threadName)s | 打印線程名稱 |
| %(process)d | 打印進程ID |
| %(message)s | 打印日誌信息 |
| %(name)s | 打印logger的名字 |
| %(module)s | 調用日誌輸出函數的模塊名 |
| %(created)f | LogRecord的創建時間,也就是當前時間,time.time() |
| %(msecs)d | LogRecord的創建時間的毫秒部分 |
| %(relativeCreated)d | 輸出日誌信息的,自logger創建以來的毫秒數 |

xxxxxxxxxxlogging.basicConfig(filename = "log.log", filemode = "w", level = logging.NOTSET, format = "%(levelname)s: %(asctime)s\t%(message)s")logging.debug("debug")logging.info("info")logging.warning("warning")logging.error("error")logging.critical("critical")輸出結果(在log.log文件中):
xxxxxxxxxxDEBUG: 2025-08-11 23:39:52,686 debugINFO: 2025-08-11 23:39:52,686 infoWARNING: 2025-08-11 23:39:52,686 warningERROR: 2025-08-11 23:39:52,686 errorCRITICAL: 2025-08-11 23:39:52,686 critical5 random:隨機模塊
💡 作用:用於實現各種分布的偽隨機數生成器,可以根據不同的實數分布來隨機生成值
5.1 random.random() 產生大於0且小於1之間的小數

xxxxxxxxxxprint(random.random())輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx0.96214436290632975.2 random.uniform() 產生指定範圍的隨機小數

xxxxxxxxxxprint(random.uniform(1,3))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx1.5026112547459635.3 random.randint() 產生指定範圍內的隨機整數(含首尾)

xxxxxxxxxxprint(random.randint(1,9))輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx95.4 random.randrange(start, stop, [step])
產生start,stop範圍內的整數,包含開頭但不包含結尾
step:指定產生隨機的步長,隨機選擇一個數據

xxxxxxxxxxprint(random.randrange(2,9,3)) # 這裡只能產2,5,8print(random.randrange(2,10,2)) # 這裡只能產2,4,6,8輸出結果:
xxxxxxxxxx86導航連結:
| 目的地 | 超連結 |
|---|---|
| 首頁 | 返回主頁 |
| Python學習 | Python學習 |
| 上一篇 | 23 - 正則進階 |
| 下一篇 | 25 - Linux基本命令 |